september 24, 2021 - ESA
ESA/Hubble Picture of the Week Prompts New Understanding of Einstein Ring
In December 2020 the ESA/Hubble team published a stunning view from the NASA/ESA #hubble Space Telescope of one of the most complete Einstein rings ever discovered. This observation has since been used to develop a lensing model to study the physical properties of the lensed galaxy. Scientists have successfully measured the distance to the object and determined the magnification factor to be 20, which effectively makes Hubble’s observing capability equivalent to that of a 48-metre telescope.
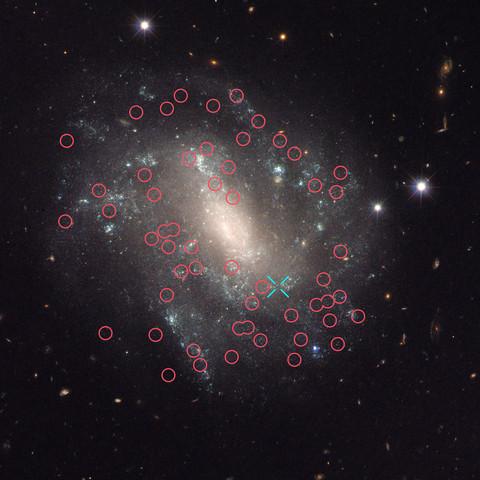
In December 2020 ESA/Hubble published an image in the Picture of the Week series depicting GAL-CLUS-022058s, located in the southern hemisphere constellation of Fornax (The Furnace). The image shows the largest and one of the most complete Einstein rings ever discovered, and was nicknamed the "Molten Ring'' by the #hubble observation’s Principal Investigator, which alludes to its appearance and host constellation.
First theorised to exist by Einstein in his general theory of relativity, this object’s unusual shape can be explained by a process called gravitational lensing, which causes light shining from far away to be bent and pulled by the gravity of an object between its source and the observer. In this case, the light from the background galaxy has been distorted into the curve we see by the gravity of the galaxy cluster sitting in front of it. The near exact alignment of the background galaxy with the centre of the galaxy cluster, seen in the middle of this image, has warped and magnified the image of the background galaxy into an almost perfect ring. The gravity from the galaxies in the cluster is soon to cause additional distortions.
A team of European astronomers have now used a multi-wavelength dataset, which includes inputs from the NASA/ESA #hubble Space Telescope and this featured image, to study this Einstein ring in detail. Archival data from the European Southern Observatory's Very Large Telescope (VLT) FORS instrument determined the redshift value of the lensed galaxy.
“In order to derive the physical properties of the lensed galaxy a lensing model is needed. Such a model could only be obtained with the #hubble imaging,” explained the lead investigator Anastasio Díaz-Sánchez of the Universidad Politécnica de Cartagena in Spain. “In particular, #hubble helped us to identify the four counter images and the stellar clumps of the lensed galaxy, for which the Picture of the Week image was used.”
From this lensing model the team calculated the amplification factor, which is a valuable effect of gravitational lensing. This allowed the team to study the intrinsic physical properties of the lensed galaxy. Of particular interest is the determination of the galaxy’s distance, which shows that the galaxy’s light has travelled approximately 9.4 billion light-years.
Further information in the press release to download














 Italian
Italian  Share
Share Share via mail
Share via mail  Automotive
Automotive Sport
Sport Events
Events Art&Culture
Art&Culture Design
Design Fashion&Beauty
Fashion&Beauty Food&Hospitality
Food&Hospitality Technology
Technology Nautica
Nautica Racing
Racing Excellence
Excellence Corporate
Corporate OffBeat
OffBeat Green
Green Gift
Gift Pop
Pop Heritage
Heritage Entertainment
Entertainment Health & Wellness
Health & Wellness